After the record-breaking trailer orders recorded in Q4 last year, new orders were down 52%, dropping from 29,500 in March to 14,400 in April.
Frank Maly, Director of Commercial Vehicle, Transportation Analysis and Research at ACT Research, shared his thoughts on the orders:
“Given the dramatic market impact of COVID shutdowns that occurred at this point last year, year-over-year comparisons provide minimal insight. Year-to-date net order volume of just over 102,000 trailers, up 164% versus last year, gives us a better metric that indicates fleet equipment demand remains strong. Strong fleet commitments, pushing the average backlog for dry vans and reefers into Q2 of 2022 at recent production rates since some OEMs have indicated that they are not accepting orders until longer-term component and materials supplies and pricing can be determined.”
Find loads and trucks on the largest load board network in North America.
Note: All rates exclude fuel unless otherwise noted.
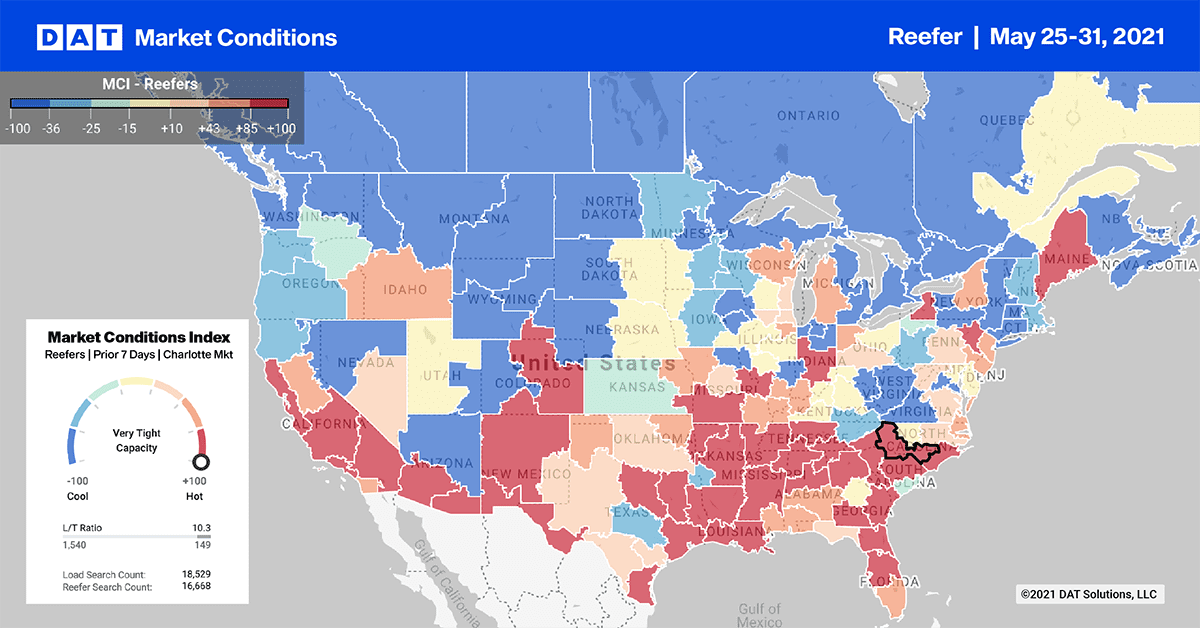
The Top 10 outbound volumes surged last week ahead of the Memorial Day holiday weekend and the reopening of the economy. Load post volumes increased by 14% while rates jumped $0.12/mile to an average of $3.26/mile.
Produce markets dominated the week again with the Lakeland, FL, market reporting a 7% increase in volumes and very tight reefer capacity with rates increasing by $0.19/mile to $2.68/mile.
In Fresno, volumes were up 9%, which resulted in even tighter capacity as rates increased by another $0.10/mile to $3.35/mile last week.
Spot rates
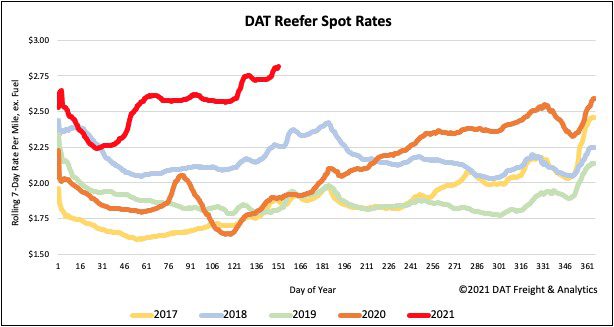
Reefer capacity tightened even more last week with spot rates jumping $0.09/mile to $2.86/mile. Reefer spot rates are still at record-high levels and now $0.92/mile higher this time last year and $0.57/mile higher than this time in 2018.
How to interpret the rate forecast:
- Ratecast: DAT’s core forecasting model
- Short Term Scenario: Formerly the pessimistic model that focuses on a more near-term historical dataset
- Blended Scenario: More heavily weighted towards the longer-term models
- Blended Scenario v2: More heavily weighted towards the shorter-term models